Hybrid Bridge
This is a PCL library that lets you connect JavaScript on the browser side to the C# side by proxying C# code.
Table of Content
- WHERE TO FIND
- HOW IT WORKS
- HOW TO USE
- BRIDGE CONTROLLER (HybridBridge.BridgeController)
- CLASS BRIDGE (HybridBridge.ClassBridge)
- HybridBridge.HybridMessagingHandler
- LIMITATIONS
- DOCUMENTATION
- LICENSE
WHERE TO FIND
This library is available as a NuGet package at nuget.org.
For this library to be usable you need to use one of the following platform packages.
HOW IT WORKS
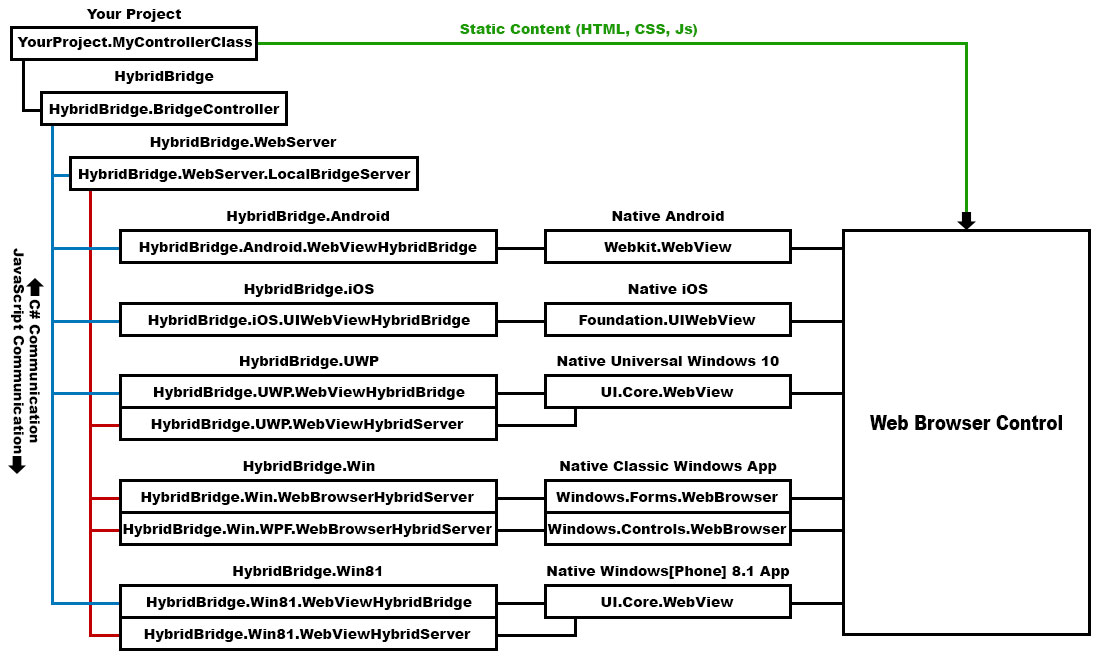
Unlike the majority of other libraries out there, HybridBridge put the focus on the JavaScript side instead of C# code. Using HybridBridge you can proxy your C# code on the JavaScript side and as result of this, you have full access to the C# class properties, methods, fields, and events.
Starting point of this library is the HybridBridge.BridgeController class which is a simple list of HybridBridge.IBridgeHandler implemented classes. Each HybridBridge.IBridgeHandler registered to this class will have the chance to response to the JavaScript side and this makes it easy to expand this library by simply writing new classes implementing HybridBridge.IBridgeHandler interface.
We also defined and shipped three class implementing HybridBridge.IBridgeHandler interface in this library, one for proxying C# classes (HybridBridge.ClassBridge), one for proxying C# enums (HybridBridge.EnumBridge) and another one just for two-way communication (HybridBridge.HybridMessagingHandler). In most cases, these are enough for your project and there is no need to write a new one.
On the other side, HybridBridge.BridgeController needs to be connected to the native Web Browser controls on each platform. This is done by inheriting this class in platform projects and packages. So you can share your JavaScript, C# code and Html files across all platforms and leave it to the platform packages to make the connection between native Web Browser control and the HybridBridge.BridgeController class.
This makes it possible to have a two-way communication between C# side and the browser (JavaScript) without any change to the logic of your program.
Following flowchart, tries to show the relationships between classes and the way communication and content delivery works in a cross-platform application using HybridBridge:
HOW TO USE
After adding the correct package to your project, it is possible to map the native Web Browser control to the HybridBridge class using the platform specific children of the HybridBridge.BridgeController class. Following examples demonstrate how to create a new instance of this classes and pass the native Web Browser control to be bridged.
Android
HybridBridge.Android package contains a class named WebViewHybridBridge inheriting from HybridBridge.BridgeController. Using this class, you are able to connect the WebKit.WebView control to the HybridBridge library.
var hybridBridge = new HybridBridge.Android.WebViewHybridBridge(webView);iOS
HybridBridge.iOS package contains a class named UIWebViewHybridBridge inheriting from HybridBridge.BridgeController. Using this class, you are able to connect the Foundation.UIWebView control to the HybridBridge library.
var hybridBridge = new HybridBridge.iOS.UIWebViewHybridBridge(webView);Universal Windows 10 Store Application (Windows 10 and Windows Phone 10)
HybridBridge.UWP package contains a class named WebViewHybridBridge inheriting from HybridBridge.BridgeController. Using this class you are able to connect the UI.Core.WebView control to the HybridBridge library.
var hybridBridge = new HybridBridge.UWP.WebViewHybridBridge(webView);Unfortunately, because of limitations forced on us by the WebView control, WebViewHybridBridge cannot offer the full functionalities of this library. For more information about this please read the Windows Store and Windows Phone WebView limitations part.
As a workaround, however, HybridBridge.UWP offers another way of connecting the HybridBridge library to the WebView, enabling it to work in full capacity; WebViewHybridServer class is responsible for enabling full two-way communication in this situations by opening a local port and handling HTTP request directly.
However, for being able to use this class, you should add the Internet Server or Private Server capacity to your application's manifest file.
var hybridBridge = new HybridBridge.UWP.WebViewHybridServer(webView);Universal Windows 8.1 Store Application and Windows Phone 8.1 Applications
HybridBridge.Win81 package contains a class named WebViewHybridBridge inheriting from HybridBridge.BridgeController. Using this class you are able to connect the UI.Core.WebView control to the HybridBridge library.
var hybridBridge = new HybridBridge.Win81.WebViewHybridBridge(webView);Unfortunately, because of limitations forced on us by the WebView control, WebViewHybridBridge cannot offer the full functionalities of this library. For more information about this please read the Windows Store and Windows Phone WebView limitations part.
As a workaround, however, HybridBridge.Win81 offers another way of connecting the HybridBridge library to the WebView, enabling it to works in full capacity; WebViewHybridServer class is responsible for enabling full two-way communication in this situations by opening a local port and handling HTTP request directly.
However, for being able to use this class, you should add the Internet Server or Private Server capacity to your application's manifest file.
var hybridBridge = new HybridBridge.Win81.WebViewHybridServer(webView);Windows Classic Applications (Windows Forms and Windows Presentation Foundation, WPF)
HybridBridge.Win package contains two class inheriting from HybridBridge.BridgeController making this possible to connect the Windows.Forms.WebBrowser and Windows.Controls.WebBrowser controls to the HybridBridge library.
However, this is important to clarify that none of these controls are natively compatible with HybridBridge mechanism for handling the request and as result of this, both classes defined in this package are working by opening a local port and listening for incoming HTTP request. This may opens a Security Hole to your application while running under Windows.
Also, you should take care of permissions required for opening a local port on the running system.
Windows Forms (WinForm)
WebBrowserHybridServer class is responsible for making the connection to the Windows.Forms.WebBrowser control:
var hybridBridge = new HybridBridge.Win.WebBrowserHybridServer(webBrowser);Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF)
WPF.WebBrowserHybridServer class is responsible for making the connection to the Windows.Forms.WebBrowser control:
var hybridBridge = new HybridBridge.Win.WPF.WebBrowserHybridServer(webBrowser);
BRIDGE CONTROLLER (HybridBridge.BridgeController)
HybridBridge.BridgeController is an abstract class handling and controlling the flow of information in the two-way communication channel between C# and JavaScript.
HybridBridge.BridgeController and all its child platform classes do support the following methods:
-
HybridBridge.BridgeController.Add(): Adds a newIBridgeHandlerinstance to the list of request handlers. This is important to note that in theHybridBridge.BridgeControllerabstract class and all its children, unless overridden, it is only possible to have one instance of a type. -
HybridBridge.BridgeController.Clear(): Clears the list ofIBridgeHandlers -
HybridBridge.BridgeController.Contains(): Returns true if the passed instance ofIBridgeHandleris in the list -
HybridBridge.BridgeController.Remove(): Removes the passed instance of theIBridgeHandlerfrom the list -
HybridBridge.BridgeController.Get<T>andHybridBridge.BridgeController.Get(): Returns the requestedIBridgeHandlerby type -
HybridBridge.BridgeController.ExecuteJavaScript(): Execute a JavaScript string and return the result. This method also accepts a callback for asynchronies execution. -
HybridBridge.BridgeController.FireJavaScript(): Executes a JavaScript string and leaves the result. This method is asynchronies by design. -
HybridBridge.BridgeController.CallJavaScriptFunction(): Calls a JavaScript function and returns the result. This method is synchronizing by design. -
HybridBridge.BridgeController.CallJavaScriptAction(): Calls a JavaScript function and leaves the result. This method is asynchronies by design.
CLASS BRIDGE (HybridBridge.ClassBridge<T>)
HybridBridge.ClassBridge<T> is a generic class implementing the IBridgeHandler interface allowing the user to be able to proxy a C# class on the JavaScript side.
This class is capable of proxying methods, fields, constants, properties, and events; providing the JavaScript side with the ability to call, get, set and subscribe to and from methods, events and properties asynchronicity and synchronicity.
Consider the following controller class for next samples:
namespace MyProject.Controllers
{
public class MyController
{
public static const int MyIntConst = 10;
public static event Action<int> MyStaticEvent;
public static int MyStaticIntProperty { get; set; };
public static MyModel MyStaticComplexFields;
public static string MyStaticMethod(string someStringValue)
{
// Do something with someStringValue variable
}
public void MySampleMethod()
{
// Do something
}
public MyController(int ctorArgument)
{
// Do something with ctorArgument and create a new instance
}
}
}Methods
Calling class methods is possible in both asynchronous and synchronize ways. The result of the method execution is also available; however, no out or ref parameters are supported. Also special methods such as the ones with await keyword are not officially supported.
C# code to add the proxy class to the JavaScript side:
var myControllerBridge =
new HybridBridge.ClassBridge<MyProject.Controllers.MyController>();
hybridBridge.Add(myControllerBridge);JavaScript code to call the method and get the return value:
var methodReturnValue =
MyProject.Controllers.MyController.MyStaticMethod(someStringValue);or asynchronously:
MyProject.Controllers.MyController.MyStaticMethodAsync(someStringValue, function (methodReturnValue) {
// propertyValue has the value of the property
});Properties
It is possible to access and change property values; this library also supports properties with custom setter and getter methods.
C# code to add the proxy class to the JavaScript side:
var myControllerBridge =
new HybridBridge.ClassBridge<MyProject.Controllers.MyController>();
hybridBridge.Add(myControllerBridge);JavaScript code to access the property value:
var propertyValue =
MyProject.Controllers.MyController.MyStaticIntProperty;or
var propertyValue =
MyProject.Controllers.MyController.get_MyStaticIntProperty();or asynchronously:
MyProject.Controllers.MyController.get_MyStaticIntPropertyAsync(function (propertyValue) {
// propertyValue has the value of the property
});JavaScript code to set the property value:
MyProject.Controllers.MyController.MyStaticIntProperty = newValue;or
MyProject.Controllers.MyController.set_MyStaticIntProperty(newValue);or asynchronously:
MyProject.Controllers.MyController.set_MyStaticIntPropertyAsync(newValue, function () {
// Indicates that the setter called successfully
});Fields
Accessing fields and constants are as easy as accessing properties; however, there is no way to directly call setter or getter methods or to interact with fields asynchronously. Constants, on the other hand, are directly reflected on the JavaScript side as a variable.
C# code to add the proxy class to the JavaScript side:
var myControllerBridge =
new HybridBridge.ClassBridge<MyProject.Controllers.MyController>();
hybridBridge.Add(myControllerBridge);JavaScript code to access a field or a constant value:
var constValue = MyProject.Controllers.MyController.MyIntConst;JavaScript code to change a field value:
MyProject.Controllers.MyController.MyIntConst = newValue;Events
Subscribing and unsubscribing to and from an event is little different from the way it is in C#. For doing so you need to use the add_{event} and remove_{event} methods or access the event like a field.
C# code to add the proxy class to the JavaScript side:
var myControllerBridge =
new HybridBridge.ClassBridge<MyProject.Controllers.MyController>();
hybridBridge.Add(myControllerBridge);JavaScript code to subscribe to an event:
function MyEventHandler(intValue) {
// Do something with the intValue
}
MyProject.Controllers.MyController.add_MyStaticEvent(MyEventHandler);or
MyProject.Controllers.MyController.add_MyStaticEvent(function (intValue) {
// Do something with the intValue
});It is also possible to replace all old subscriptions with a new one:
function MyEventHandler(intValue) {
// Do something with the intValue
}
MyProject.Controllers.MyController.MyStaticEvent = MyEventHandler;JavaScript code to unsubscribe an event:
MyProject.Controllers.MyController.remove_MyStaticEvent(MyEventHandler);Or remove all subscriptions altogether:
MyProject.Controllers.MyController.MyStaticEvent = null;Instances
Just like static methods, it is possible to reflect functionalities of the instances of a class on the JavaScript side. However, for doing so you need to choose the variable name on the C# side and pass it to the ClassBridge<T>.AddInstance() method.
It is also possible to not mention a variable name; this makes the instance available on the JavaScript side, however with no clear way to access it. This behavior is rarely useful.
C# code to add the proxy class and its instance to the JavaScript side:
var myControllerBridge =
new HybridBridge.ClassBridge<MyProject.Controllers.MyController>();
var controllerInstance = new MyProject.Controllers.MyController(someIntValue);
myControllerBridge.AddInstance(controllerInstance, "JavaScriptInstanceVariable");
hybridBridge.Add(myControllerBridge);On the JavaScript side, it is possible to access this instance using the variable name; following sample shows how to call a method on the reflexed instance:
JavaScriptInstanceVariable.MySampleMethod();However, it is important to know that by doing so, ClassBridge<T> keeps a reference to the instance in the memory and this may result in a memory leak if abused. So it is always a good practice to remove the instance as soon as it is no longer needed.
Check out the following sample to remove one or multiple instances from the JavaScript side using the instance’s variable name:
myControllerBridge.RemoveInstance("JavaScriptInstanceVariable");Or using the instance(s) directly. This, however, will clear all variables to this instance on the JavaScript side:
myControllerBridge.RemoveInstance(controllerInstance);Instantiating
It is possible to create a new instance of a class directly from the JavaScript side. This will call the class constructor and then adds the newly created instance automatically. It is important to use this feature with caution to prevent memory leak:
C# code to add the proxy class to the JavaScript side:
var myControllerBridge =
new HybridBridge.ClassBridge<MyProject.Controllers.MyController>();
hybridBridge.Add(myControllerBridge);And to create the new instance on JavaScript:
var JavaScriptInstanceVariable =
new MyProject.Controllers.MyController(someIntValue);
HybridBridge.HybridMessagingHandler
Using HybridBridge.HybridMessagingHandler your application can have a fast and two-way communication channel. Unlike HybridBridge.ClasBridge<T>, using this handler, you don't need to define a controller class and this makes thing a lot easier and faster.
Making a new instance of the HybridBridge.HybridMessagingHandler accessible on the JavaScript side:
var hybridMessaging = new HybridBridge.HybridMessagingHandler();
hybridBridge.Add(massagingHandler);Listen to messages with 'MyMessage' identification on C#:
hybridMessaging.Subscribe("MyMessage", () => {
// Do something
});Or on JavaScript:
HybridMessaging.Subscribe("MyMessage", function() {
// Do something
});It is also possible to return a value as the result of the message execution as well as sending an optional parameter. Following examples shows how to send a message with MyMessageWithParameter as its identification on C#:
hybridMessaging.Send("MyMessageWithParameter", someParameter);Or if expecting a string as the result and sending an int as the parameter:
var result = hybridMessaging.Send<String, Int>("MyMessageWithPrameter", someIntParameter);Or on JavaScript:
var returnValue = HybridMessaging.Send("MyMessage", someParameter);Doing same thing on JavaScript asynchronously looks like this:
HybridMessaging.SendAsync("MyMessage", someParameter, function (returnValue) {
// Do something with returnValue
});HybridMessaging variable on the JavaScript is the representation of the HybridBridge.HybridMessagingHandler instance on the C# side. However, its name can be changed by explicitly passing a different name as a string to the HybridBridge.HybridMessagingHandler constructor.
LIMITATIONS
-
outkeyword for method parameters -
refkeyword for method parameters
Windows Store and Windows Phone WebView limitations
Due to UI.Core.WebView running the JavaScript engine on the UI thread along with itself processing requests on the same thread, it is impossible to execute JavaScript methods that blocks the execution of the script as it does also block the control from receiving the request.
This means that any synchronized method or call on the proxy class is not supported; following is the list of limitations:
- Synchronized calls on method puts UI thread on deadlock and therefore not possible
- Getting or Setting property values synchronicity is not possible
- Getting or setting field values is not possible at all
- Sending synchronized messages is not possible
As the result of the above limitation, we suggest using classes that inherit the HybridBridge.LocalServer.LocalBridgeServer class letting controller opens a local port and response to the HTTP requests made from JavaScript. This makes the necessary separation from UI thread and therefore allows your code to use full functionalities of the HybridBridge library.
Following is the list of classes that are part of the HybridBridge.LocalServer.LocalBridgeServer inheritance tree:
-
HybridBridge.UWP.WebViewHybridServer: Universal Windows 10 Applications for PC and Mobile Phones -
HybridBridge.Win81.WebViewHybridServer: Universal Windows 8.1 Applications for PC and Mobile Phones -
HybridBridge.Win.WebBrowserHybridServer: Classic Windows Applications such as Windows Form and WPF
However, using above classes may make your program vulnerable to attacks targeting the local HTTP server. On the other hand, to be able to use this method, you might need to allow your program certain capacities and permissions under each platform you are targeting.
DOCUMENTATION
The project online documentation is available at github.io.
LICENSE
GNU LESSER GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
Version 3, 29 June 2007
Copyright (C) 2007 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies
of this license document, but changing it is not allowed.
This version of the GNU Lesser General Public License incorporates
the terms and conditions of version 3 of the GNU General Public
License, supplemented by the additional permissions listed below.
0. Additional Definitions.
As used herein, "this License" refers to version 3 of the GNU Lesser
General Public License, and the "GNU GPL" refers to version 3 of the GNU
General Public License.
"The Library" refers to a covered work governed by this License,
other than an Application or a Combined Work as defined below.
An "Application" is any work that makes use of an interface provided
by the Library, but which is not otherwise based on the Library.
Defining a subclass of a class defined by the Library is deemed a mode
of using an interface provided by the Library.
A "Combined Work" is a work produced by combining or linking an
Application with the Library. The particular version of the Library
with which the Combined Work was made is also called the "Linked
Version".
The "Minimal Corresponding Source" for a Combined Work means the
Corresponding Source for the Combined Work, excluding any source code
for portions of the Combined Work that, considered in isolation, are
based on the Application, and not on the Linked Version.
The "Corresponding Application Code" for a Combined Work means the
object code and/or source code for the Application, including any data
and utility programs needed for reproducing the Combined Work from the
Application, but excluding the System Libraries of the Combined Work.
1. Exception to Section 3 of the GNU GPL.
You may convey a covered work under sections 3 and 4 of this License
without being bound by section 3 of the GNU GPL.
2. Conveying Modified Versions.
If you modify a copy of the Library, and, in your modifications, a
facility refers to a function or data to be supplied by an Application
that uses the facility (other than as an argument passed when the
facility is invoked), then you may convey a copy of the modified
version:
a) under this License, provided that you make a good faith effort to
ensure that, in the event an Application does not supply the
function or data, the facility still operates, and performs
whatever part of its purpose remains meaningful, or
b) under the GNU GPL, with none of the additional permissions of
this License applicable to that copy.
3. Object Code Incorporating Material from Library Header Files.
The object code form of an Application may incorporate material from
a header file that is part of the Library. You may convey such object
code under terms of your choice, provided that, if the incorporated
material is not limited to numerical parameters, data structure
layouts and accessors, or small macros, inline functions and templates
(ten or fewer lines in length), you do both of the following:
a) Give prominent notice with each copy of the object code that the
Library is used in it and that the Library and its use are
covered by this License.
b) Accompany the object code with a copy of the GNU GPL and this license
document.
4. Combined Works.
You may convey a Combined Work under terms of your choice that,
taken together, effectively do not restrict modification of the
portions of the Library contained in the Combined Work and reverse
engineering for debugging such modifications, if you also do each of
the following:
a) Give prominent notice with each copy of the Combined Work that
the Library is used in it and that the Library and its use are
covered by this License.
b) Accompany the Combined Work with a copy of the GNU GPL and this license
document.
c) For a Combined Work that displays copyright notices during
execution, include the copyright notice for the Library among
these notices, as well as a reference directing the user to the
copies of the GNU GPL and this license document.
d) Do one of the following:
0) Convey the Minimal Corresponding Source under the terms of this
License, and the Corresponding Application Code in a form
suitable for, and under terms that permit, the user to
recombine or relink the Application with a modified version of
the Linked Version to produce a modified Combined Work, in the
manner specified by section 6 of the GNU GPL for conveying
Corresponding Source.
1) Use a suitable shared library mechanism for linking with the
Library. A suitable mechanism is one that (a) uses at run time
a copy of the Library already present on the user's computer
system, and (b) will operate properly with a modified version
of the Library that is interface-compatible with the Linked
Version.
e) Provide Installation Information, but only if you would otherwise
be required to provide such information under section 6 of the
GNU GPL, and only to the extent that such information is
necessary to install and execute a modified version of the
Combined Work produced by recombining or relinking the
Application with a modified version of the Linked Version. (If
you use option 4d0, the Installation Information must accompany
the Minimal Corresponding Source and Corresponding Application
Code. If you use option 4d1, you must provide the Installation
Information in the manner specified by section 6 of the GNU GPL
for conveying Corresponding Source.)
5. Combined Libraries.
You may place library facilities that are a work based on the
Library side by side in a single library together with other library
facilities that are not Applications and are not covered by this
License, and convey such a combined library under terms of your
choice, if you do both of the following:
a) Accompany the combined library with a copy of the same work based
on the Library, uncombined with any other library facilities,
conveyed under the terms of this License.
b) Give prominent notice with the combined library that part of it
is a work based on the Library, and explaining where to find the
accompanying uncombined form of the same work.
6. Revised Versions of the GNU Lesser General Public License.
The Free Software Foundation may publish revised and/or new versions
of the GNU Lesser General Public License from time to time. Such new
versions will be similar in spirit to the present version, but may
differ in detail to address new problems or concerns.
Each version is given a distinguishing version number. If the
Library as you received it specifies that a certain numbered version
of the GNU Lesser General Public License "or any later version"
applies to it, you have the option of following the terms and
conditions either of that published version or of any later version
published by the Free Software Foundation. If the Library as you
received it does not specify a version number of the GNU Lesser
General Public License, you may choose any version of the GNU Lesser
General Public License ever published by the Free Software Foundation.
If the Library as you received it specifies that a proxy can decide
whether future versions of the GNU Lesser General Public License shall
apply, that proxy's public statement of acceptance of any version is
permanent authorization for you to choose that version for the
Library.
